Synthetic fibres are fibres manufactured from organic polymers from many formulations: acrylic, aramid, carbon, polyester, polyethylene, and the most common nylon and polypropylene.
Synthetic fibres are engineered to withstand the long-term alkaline environment of concrete. Synthetic fibres fall in 2 categories, micro synthetic fibres or macro synthetic fibres. (Fibers, 2018). Macro fibres are so named due to their larger size.
Macro synthetic fibres, due to their length and unique design, produce an excellent mechanical bond. The macro plastic fibres can be virgin and recycled polypropylene (PP), high-density polyethylene (HDPE), or polyethylene terephthalate (PET) fibres. PP fibres have been widely used in the concrete industry, due to the ease of production and high alkaline resistance (Yin. et. al., 2015).
Representative properties from iNFORCE Radforce synthetic fibres include:
- Polyolefin polymer material
- Fibre Length 48 mm.
- Width 1.29 mm.
- Tensile Strength Min. 550 MPa
Fibres can be added during conventional mixing, e.g. 2-10 kg. per cubic meter for Radforce fibres. A 3-5-minute mix cycle provides three dimensional distribution throughout the concrete.
RADFORCE synthetic fibres are ideally suited in pre-cast, shotcrete and slabs-on-ground, among many other applications. The fibers are used to enhance properties such as crack resistance, crack control, durability, fatigue life, resistance to impact and abrasion, volume change due to moisture, thermal variations, and fire resistance.
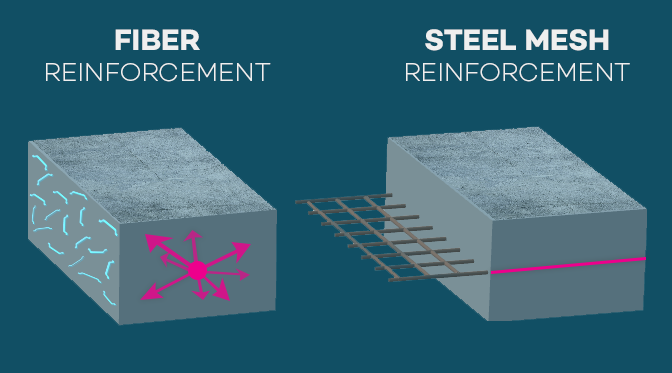
Easy handling, environmentally friendly recycled packaging leaves no waste on site as the entire package is thrown into the mix during batching. The fibre is evenly dispersed through the matrix, ensuring no balling or pumping problems will occur. This dramatically speeds up construction and reduces labour time by completely eliminating the need for steel mesh reinforcement. In combination with good design, sub-base conditions, concrete properties and placing techniques, RADFORCE fibres deliver a stronger and more durable slab with top to bottom reinforcement within the slab.
ASTM provides test methods for measuring various post-first crack performance including ASTM (C1399, C1550 and C1609). Further discussion of the benefits of synthetic fibres can be found in ACI 544.1R. ASTM Subcommittee C9.42 provides state-of-the-art reports and methods to evaluate and specify fibre reinforced concrete.
Research on using synthetic fibres in concrete began in approximately 1963. The early work by Goldfein (1963) on synthetic fibres in Portland cement led to a patent covering polyolefin fibres (e.g., polypropylene, polyethylene, nylon, polyvinyl chloride, etc.). Polyolefins are thermoplastics that are generally inexpensive, lightweight, tough, alkali resistant materials. Commercial applications as reinforcement in concrete began around 1978. To date, more than one billion square feet of synthetic fibre reinforced concrete has been successfully placed (Zeller, 1994).